Increasing the amount of insulation in a building has been named as one of the most simple and cost-effective energy-efficient measures for achieving saving. The latest energy codes drive greater energy efficiency with tighter and better-insulated buildings.
Insulation, when used properly, adds thermal comfort for the interior spaces, reduces heat loss or gain and decrease a building’s energy demand. Today’s market presents multiple solutions and systems that can be used for architectural aesthetics. From spray-on insulations to insulating materials, all these materials are evaluated using their R-Value, a value that represents the effectiveness and insulation property of the materials.

Reasons to Insulate a Building:
- Greater energy efficiency, lower energy bills: Values of energy efficiency are obvious as it saves building occupants money on energy bills and reduces power plant CO2 emissions to lower carbon footprints. The benefits continue growing its importance as energy bills rise and the public becomes more conscious of carbon impact. The energy use gets scored from 0-100 based on their performance and how efficient they are. Energy-efficient figures get recognized and capitalized based on the trends of commercial buildings that exceed code and stand out from competitors.
- Meeting occupant needs for comfort: Thermal comfort is a major driver of occupant satisfaction, and a building that is uncomfortable or has significant temperature variations is likely to result in disgruntled occupants. Insulation and ait sealing are a key to thermal comfort, and meeting code is not guaranteed of occupant satisfaction. It is easy to assume that localized control of heating and cooling satisfies occupants throughout a building with proper insulation and air sealing, meaning, the occupants will use even more energy trying to stay comfortable.
- Acoustic Impact: The body of evidence demonstrates the links between noise and workplace productivity with satisfaction. As a trend of more open workspaces, floating walls and glass elements continue growing, so does the issues of noise. Acoustic design is dependent and complex due to many building factors like -building type, location, and occupancy.
- Sustainability: It is estimated that 40-48% of new non-residential constructions will be ‘green’ & 13.8 billion square feet of building space will be LEED certified. Lease rates for ‘green’ spaces will be up to 20% above average, manifesting in high rental prices and decreased vacancy rates.
Economic Benefits:
- Insulation reduces home heating and cooling cost by 20 to 30%
- The cost of insulation pays for itself in 3 to 5 years through reduced electricity or fuel bill.
- Reduce the burden of increasing energy prices.
- The cost of insulation is not more than 1 to 3% of the total property value and last life long without any maintenance.
- The insulated building reduces the size or capacity of the HVAC system and thus minimizes capital expenditure.
Environmental Benefits:
- Energy consumption is building segment is rising at a faster rate due to rapid urbanization.
- Insulation has an immediate impact on reducing total energy demand and reducing GHG emissions.
Social Benefits:
- Properly insulated building renders to comfort and healthy living by controlling temperature noise level.
- Insulation provides an ideal environment in offices and residential buildings resulting in greater productivity.
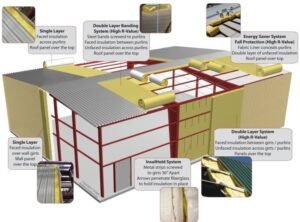
Building Insulation Materials:
Bulk insulation and reflective insulation are the most practiced insulation materials and it acts as a barrier to heat flow between the building and the outside. It can be purchased in rolls or boards, and it is typically made from glass wool, polyester, natural, wool, or recycled paper.
Insulating concrete forms are typically manufactured with polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, cement-bonded wood fiber, or cellular concrete. The forms are often permanently left in place after the concrete has cured to provide soundproofing, thermal insulation, drywall and space for electrical conduit wiring.
To know more about Architecture Technology, Stay Tuned.

