Designers and Architects in the building industry are continually looking for new innovative technologies to create livable spaces that are environmentally resilient and responsible. Always striving to look for inspiration from nature- a discipline known as biomimicry.
“Creative and innovative technologies in architecture are continuously developing.”
From its infinite complexity, nature is an inspirational influence that expands the aesthetic horizons of the building development. The mission now is to recover the fragile threads with nature that have been lost for almost a century now.
What is Biomimicry?
From a literal translation of the word, Bios – Life and mimesis – To imitate
The term biomimetic was first introduced by Otto Schmit in 1982 and rediscovered by Janine Benyus in 1997 – an innovation consultant and co-founder of Biomimicry Institute. Mimicking natural systems or processes would affect the form, which wasn’t the fundamental point in biomimicry. And biomimetic is practiced through learning from nature for improvement of technology.
When first defined, Biomimicry is an ‘innovation inspired by nature’. Biomimicry has been a new discipline in architecture and engineering for the past thirty years, in a practical sense. Development in technology and material science enabled the growth of Biomimicry.

A source of inspiration:
- Curiosity: As designers are curious, biomimicry provides them the opportunity to learn about life’s water, energy and materials.
- Beyond form: Looking for inspiration in nature, from Greek columns to Santiago Calatrava’s iconic structures, Biomimicry has always challenged the sustainability strategies of a structure. But the practice of biomimicry looks beyond the form that fits form to function.
- Accomplishing multiple objectives: Similar to like trees provide shade with their leaves, generates energy, bark helps in protecting and cool the water beneath the surface. Imagine, buildings accomplishing the attributes like a multi-functional design.
- Adapting to context and climate: Instead of fighting against climate by using energy resources, it shall adapt to the changing seasons with the availability of materials and energy.
- Enhance ecosystem services: Streets, parks, open spaces can be constructed to perform the same functions as a natural ecosystem does like – stormwater harvesting, flood mitigation, energy-efficient buildings, habitat creation. We can at least create a built environment that ‘fits in’.
- Embody resilience: Adapting to changing needs that fit its context, incorporating biodiversity and embodying resilience through innovative techniques.
The relationship between nature, technology, and architecture is an ancient debate with many historical bits and pieces attached to it resulting in paradigm shifts. Our interpretation of the latest works is mostly conjecture. While some interpreting biomimicry as an all-encompassing approach to learning from nature. Biomimicry has always been a process of being either problem based, from design problem to biology, or solution-based, from biology to design.
The debates on environmental impact and sustainability influenced architecture through new innovative measures that are viable on energy-efficient with the environmental impact of buildings during and after construction. Architectural practices continue to search for more sustainable design concepts, energy-efficient, zero energy, green, and intelligent building construction methods concepts.
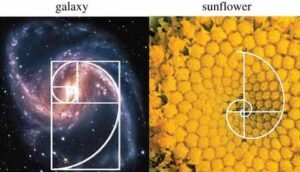
Leonardo da Pisa nicknamed Fibonacci, a sequence of numbers approached the golden ratio. The technique was used in identifying Fibonacci numbers in nature including the sequence and patterns on pineapples, sunflower, seashells, and arrangement of petals in dahlia flower. The proportions of the golden ratio are not only in living nature but also in the entire universe from the smallest to the largest scale.
Benefits of Biomimicry:
Scientists, architects, and engineers take inspiration from living nature for the purpose of functionality and form. They incorporated many bioinspired ideas in both ornamentation and functional ways, developing design strategies by incorporating patterns and organizations found in natural forms.
Biomimicry emphasis on problem-solving distinguishing it from concepts like biophilia (the innate need for connections with nature and other forms of life), biomorphism (design based on nature’s shapes and forms), bio-utilization (direct use of nature for green infrastructure) and bio-inspired design.
The concept of biomimesis has been used in chemistry for compounds with enzyme-like catalytic action. Some benefits of using biomimetic materials include:
- Are sustainable: Self-assemble, optimize, cross-pollinate, adapt, evolve, and use free energy. By following the principles of life uses, products and processes can be created that adapt to life on earth.
- Perform well: A design strategy is not effective when its carrier dies. But nature has strategies for 3.8 billion years. Biomimicry helps you study the successful strategies so you can thrive in your market as it thrived in their habitat.
- Save energy: Energy is nature is more expensive than in the human world. Plants have to trap sunlight and convert and the predators hunt and catch it. These efficient strategies dramatically reduce the energy for use.
- Cut material costs: As nature builds to shape, the shape is cheap and the material is expensive. Using biomimetic materials, it can minimize the amount of your company spending while maximizing the effectiveness of your products and forms to achieve desired functions.
Bio-inspired is not just a consequence of observation of naturally occurring structures but a boundary of conditions in which the development is observed. Furthermore, one might argue that the qualities of the material are focused on sustainability, while the other might focus on aesthetics and visualization.
A change can be noticed now! Buildings are more shaped like the natural world than age-old rectilinear boxes have always dominated the architectural history. And yet, the potential for architects to learn more deeply from nature, and use biomimetic materials and technologies is still developing. Bioarchitecture or biomimicry as a practice can provide a benefit of scientific opportunities when presented without amalgamation.
To know more about Architecture Technology, Stay Tuned. Till then, you can visit the Security Awareness Section for day-to-day cyber attacks and how to prevent them.