[speaker id=28747]
Emotet, an advanced, self-propagating, modular Trojan is back after a long “spring break” with some new nasty tricks and has started affecting various devices. Various Cyber – Security companies has noticed growth of this attack after spring. During summer the attacks of Emotet were reduced by 50%. However, holidays didn’t last long, and Emotet, typically distributed via email, has found new ways to avoid detection and is once again among the most dangerous malware.
What is Emotet ?
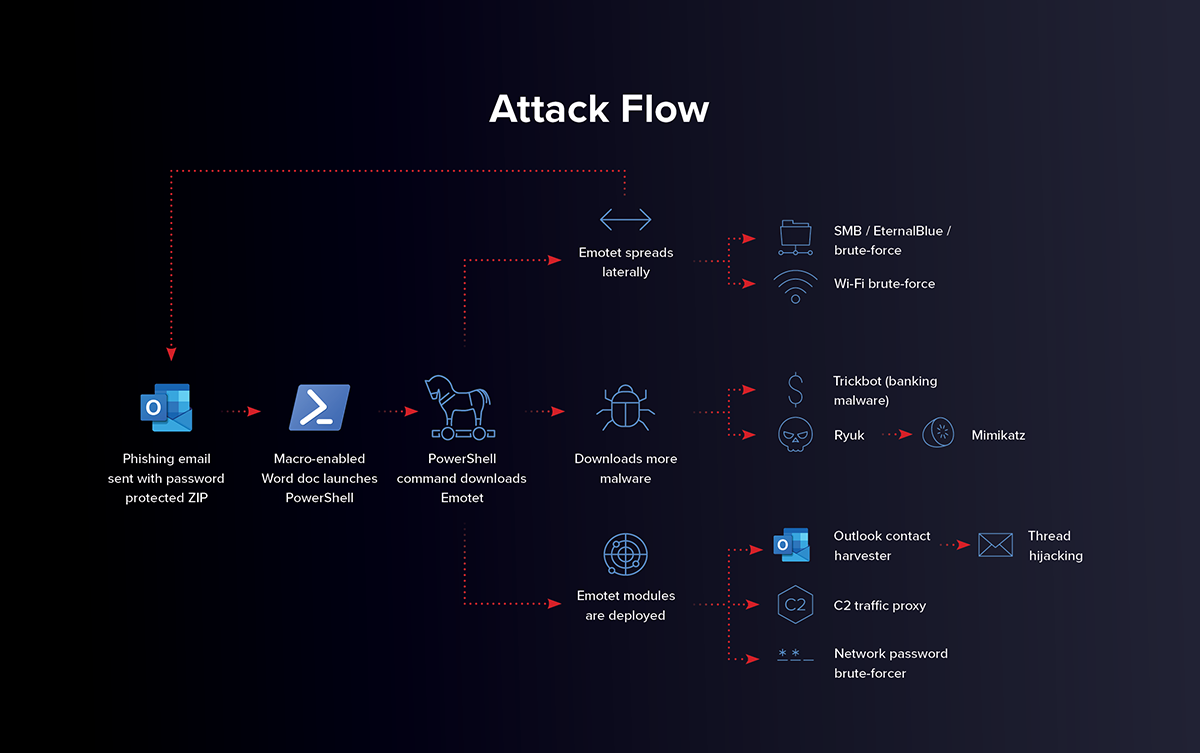
Emotet is an advanced, self-propagating, modular Trojan that is primarily spread through spam emails. The infection may arrive either via malicious script, macro-enabled document files, or malicious link. E – mails which are embedded with Emotet contains familiar branding designed to look like a legitimate email. Emotet tries to persuade users to click on the file and download it by using tempting languages like “Your Invoice”, “Payment Details” or possible upcoming shipment from a well – known parcel company.
Everyone is a target for Emotet. To date, Emotet has hit individuals, companies, and government entities across the United States and Europe, stealing banking logins, financial data, and even Bitcoin wallets.
New Trick of Emotet ?

According to Cyber – Security researchers, this new phishing attack may be the result of Microsoft’s action by disabling specific macros associated with Ms Office Apps. The change in macros resulted in prevention of attackers from targeting document with automation to execute malware on victim’s system.
As per cybersecurity researchers, the new techniques observed in recent campaigns appeared to be tested on a smaller scale, as a test for potential be used for a larger campaign. The new campaigns use compromised email accounts to send out spam phishing emails with one – word tempting headlines like “Your Invoice”, “Payment Details”, “Salary”, used to encourage users to click and open the email out of curiosity, which leads to deploy malware and compromise windows system.
The message body contains a OneDrive URL. This URL hosts Zip files containing Microsoft Excel Add-in (XLL) files with a similar name to the email subject line. If these XLL files are opened and executed, Emotet will infect the machine with malware. Further, it can steal the information or create a backdoor for deploying other malware to compromise the Windows system.
The use of OneDrive URLs and XLL makes this campaign distinct from previous ones. Earlier Emotet attempted to spread itself via Microsoft Office attachments or phishing URLs. Those malicious payloads included Word and Excel documents containing Visual Basics for Applications (VBA) scripts or macros.
How to Protect Emotet from getting hit ?
To prevent from Emotet getting hit on your device, you should follow all the steps given below,
- Keep your computer/endpoints up to date with the latest patches for Microsoft Windows.
- Do not open or download suspicious emails, links or images. If you are unsure that the email is fake, do not take risk to sender.
- If you are asked to allow a macro to run on a downloaded file, do not do so under any circumstances, but delete the file immediately. This way you will not give Emotet a chance to get on your computer in the first place.
- Back – up your important data to an external Hard – drive regularly. In case of data breach, you will have all you imported infected data.
- Use strong passwords for all the accounts logins. And a strong password does not include you Pets name or any other which may be reveled easily. Only use combinations of Numbers, Alphabets and special characters. This keeps your passwords protected.
- Use Two – Factor Authentication in all the accounts.
How to Remove Emotet after getting Hit ?
First of all, don’t panic if you suspect that your PC may be infected with Emotet. Inform your personal circle about the infection, because people in your email contacts are potentially at risk.
Next be sure to isolate your computer if it is connected to a network to reduce the risk of Emotet spreading. Subsequently, you should change all the login data for all your accounts (email accounts, web browsers, etc.) Do this on a separate device that is not infected or connected to the same network.
Because Emotet is polymorphic (meaning that its code changes slightly each time it is accessed), a cleaned computer can be quickly re-infected if it is connected to an infected network. Therefore, you must clean all computers connected to your network — one after the other. Use an antivirus program to help you do this. Alternatively, you can also contact a specialist, such as your antivirus software provider for guidance and help.

