Android applications are seen to be most vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Moreover, the rise in operations of applications for the last three months has given cyber crooks a large number of potential targets. Recently, ThreatFabric security firm has traced a new banking malware, dubbed as the BlackRock Trojan, affecting 337 android apps including major financial, networking, communication, dating, and social apps to steal banking credentials.
First detected in May 2020, the BlackRock malware is known to belong to the LokiBot malware family targeting banking apps to steal data and credentials. But the present trojan is seemingly spreading its scope by targeting a plethora of non-financial apps. Moreover, to raise no alarms the trojan tricks the android users by presenting itself as a Google Update and thus, compromising the device.
The Malware Family
The BlackRock Trojan is based on the code source of Xerxes banking Trojan, a malware emerged in May 2019. The latter itself is a LokiBot descendant with other variants appeared in the yesteryears.

The source code of the Xerxes banking Trojan was publicly published in May 2020, making it available to other threat actors. But there no trace of any campaign based on the publicly published code, until BlackRock arrived. BlackRock Trojan is the only Android malware appeared based on the Xerxes malware.
Unlike the other predecessors of the LokiBot malware family, the malware is employing new techniques including the ability to bring changes in its code. The LokiBot and the variants were primarily focused on targeting financial apps but the BlackRock Trojan has annexed its target lists by adding a large number of non-financial Android applications.
According to researchers at ThreatFabric, the number of social, networking, communication and dating applications targeted so far were not seen in target lists of the other LokiBot malware variants. This indicates that the threat actors behind the attacks are trying to abuse the grow in the online socializing that is growing rapidly due to the pandemic.
BlackRock Trojan Target List
The malware has affected a series of most used apps getting a total of 337 android apps. These include Gmail, Microsoft Outlook, Google Play Store, Uber, Amazon, eBay, Netflix, and Cash App. The target list also contains cryptocurrency apps- Coinbase and Binance.
The other apps for stealing credentials include Twitter, Skype, Snapchat, Telegram, Whatsapp, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, Reddit, TikTok, Tinder and Grindr.
It’s also targeted various banking apps in an effort to steal credentials, including:
- Barclays
- Santander
- Royal Bank of Scotland
- Lloyds
- ING
- Wells Fargo.
How It Works?
The malware is believed to enter a device through applications downloaded through third-party app stores. After getting installed on the device the application hides from the app drawer, making it invisible to the end-user. In its second step, the BlackRock Trojan poses as fake Google Update asking the victim to provide Accessibility Service privileges.
After the victim provides the privileges, BlackRock begins granting itself all necessary permissions to operate all its nefarious activities without letting the victim known anything. When the additional permissions are granted BlackRock Trojan no longer needs user interaction and can interact with the C2 servers and launch its overlay attacks.
BlackRock Trojan Features
The Trojan offers a range of malicious features including spamming, sending and stealing SMS, recording keystrokes, lock the victim on the HOME screen, steal and hide notifications, prevent the Antivirus from functioning.
To establish persistency, the trojan restricts/redirects the user to the HOME screen incase the Antivirus (including Avast, AVG, BitDefender, Eset, Symantec, TrendMicro, Kaspersky, McAfee, Avira) or any Android cleaning app (such as TotalCommander, SD Maid or Superb Cleaner) is tried to be opened.
Abusing DPC
Device Policy Controller (DPC) is an Android feature which enables companies to control and apply policies without administrative permissions on the device. BlackRock Trojan exploits this feature by creating and attributing itself a profile with admin privileges.
Overlay Attacks
The most notorious of all, the ability to check the apps running in the foreground. By exploiting the Accessibility Service BlackRock Trojan can record the foreground running apps.
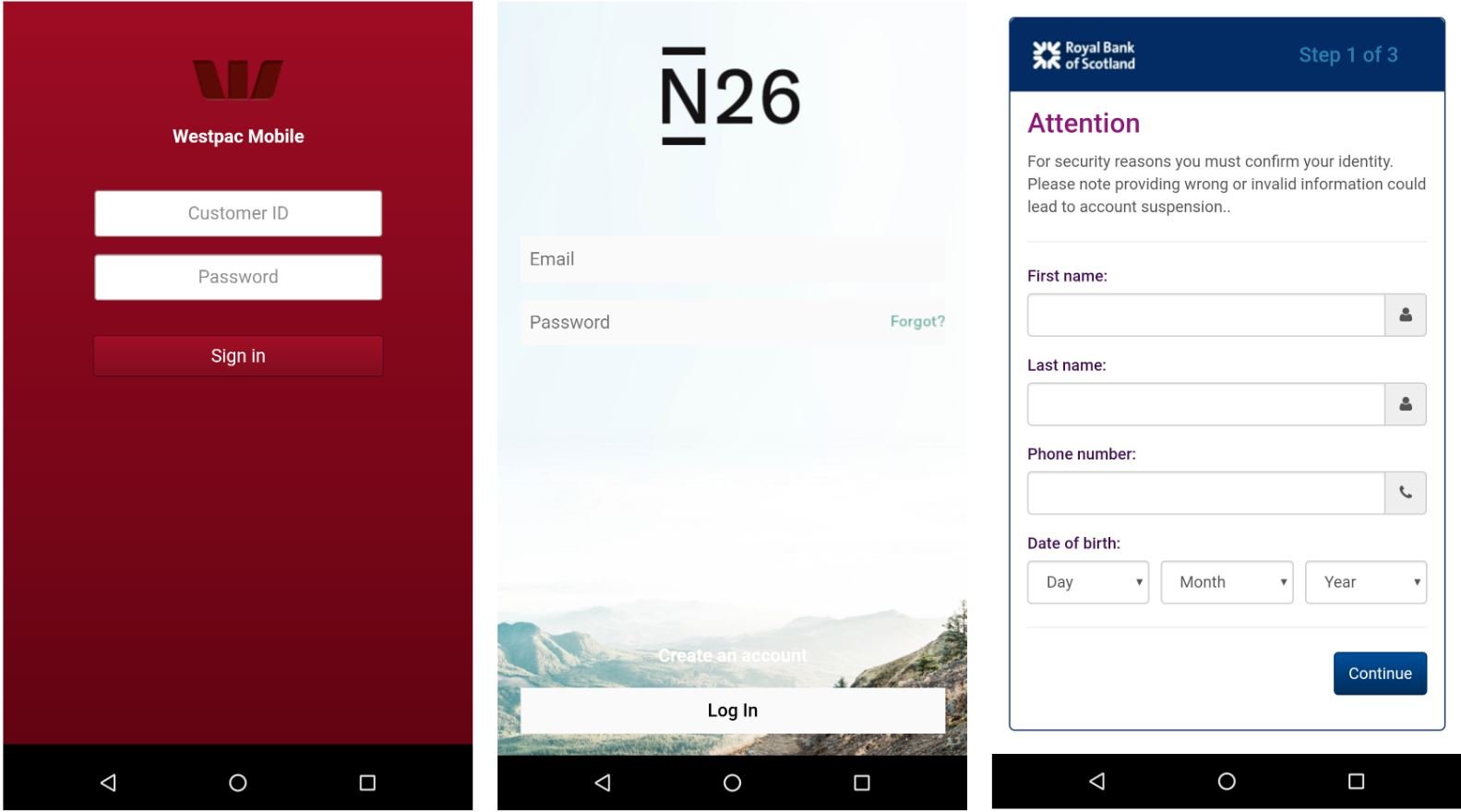
BlackRock Trojan uses two overlay screens: generic card grabber view and the other is credential phishing overlay- for specific targeted applications. This enables the Trojan to download an archive of all the overlays files on the infected device.
Interestingly, the 337 targetted apps include non-financial apps to steal banking credentials. Researchers said that this was done seeing the rise in socialisation during the COVID times. For the credential-phishing overlays, the apps targeted are related to banks operating in Europe, followed by Australia, the United States of America and Canada.
Researchers have not found the malware on the Google Play Store. So the best bet is to download apps only from the original Google Play Store and granting permissions to apps carefully.
The patch for it could be on the way!


