Buildings are a huge source of energy consumption and greenhouse gases emission. Of the energy consumed by buildings, 50% was used for space heating and cooling purposes. Therefore, the conservation of heating and cooling energy presents a major target for building energy conservation. Although majorly buildings are insulated for thermal purposes, it also provides lucrative solutions for fire, acoustic and impact concerns. Often insulating materials are used and selected on the basis of its ability to satiate several of these functions at a time. After proper air sealing, insulation is one of the most important features of a building to reduce energy consumption and provide thermal comfort.

Thermal insulation means the use of appropriate insulation materials and design adaptations for buildings to slow the transfer of heat through the enclosure to reduce heat loss and gain. The transfer of heat may be caused by the temperature difference between indoors and outdoors. Heat may be transferred either through conduction, convection, or radiation.
The rate of transmission is closely connected to the propagating medium. Heat is lost or gained by transmissions through the ceilings, walls, floors, windows, and/or doors. It not only increases the load on the HVAC system resulting in more energy wastage but also reduces the thermal comfort of people in the building. Thermal insulation in buildings is an utmost priority in achieving thermal comfort for its occupants. Insulation reduces unwanted heat loss or gain and can diminish the energy demands of heating and cooling systems.
If you consider using a green source of energy for your building, viz solar panels, solar heating, hand pumps, etc, the prima uno would be thermally insulating your homes and buildings. This ensures the full utility of natural resources and not waste any energy. If this step is skipped, it ends up demanding an expensive, powerful, and energy-consuming ventilation system, which will put a heavy load on the energy resources. Thermal insulation is one of the most efficient and easy ways to maintain thermal decorum and reduce the stress on energy resources and help slower their depletion. Thermal insulation aims to minimize the heat transfer between outside and inside of the building.
Ways to Improve Insulation:
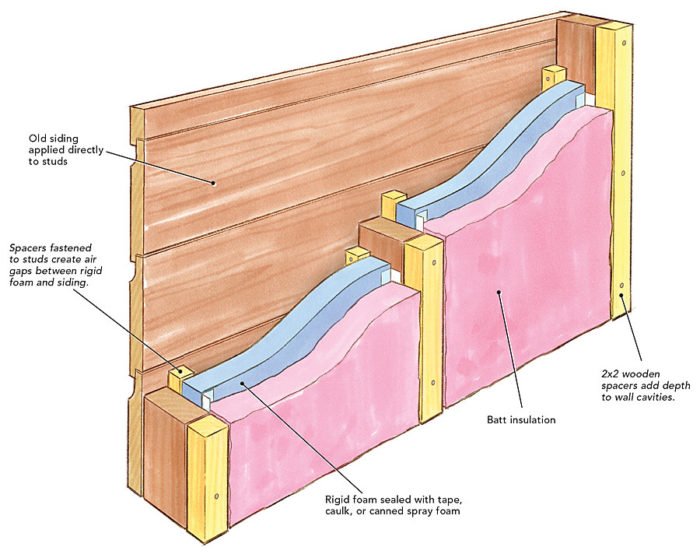
- Insulating the walls, floors, and attic
- Sealing any air leaks
- Insulating the ducts
- Reflective insulation (Radiant barrier)
Technologies and Strategies for the Different Climates:
Cold Climate Zone
Strategies in Cold Climate Zone
In cold conditions, the main aim is to reduce the heat flow out of the building. The components of a building component- windows, door, floors/foundation, walls, and air filtration barriers- are all important sources of heat loss. Losses can be decreased using good weatherization, bulk insulation, and reducing the use of non-insulated glazing.
Technologies Used in Cold Climate Zone
Vacuum Panels and Aerogel Wall Surface Insulation are two technologies that can enhance the energy performance and thermal insulation effectiveness of the residential and commercial buildings in the cold climate zones. In the cold climate zones, there high chances of heat losses due to the cold climate (infiltration, ventilation, and radiation). Hence these are the two technologies that are worth a shot.
Hot Climate Zones
Strategies in Hot Climate Zones
In hot regions, the major source of heat energy is solar radiation. This can either enter buildings directly through the windows or heat the building shell to a higher temperature than the ambient, increasing the heat transfer through the building envelope. Solar gain can be reduced by an ample amount of shading from the sun, light coloured roofing, spectrally selective (heat-reflective) paints and coatings, and various types of insulation for the rest of the envelope. Radiant barriers are highly effective for attic spaces in hot climates. In this application, they are much more effective in hot climates than cold climates. Radiant barriers must face an adequate air-gap to be effective.
Technologies Used in Hot Climate Zones
A new technology called Cool Roof has been introduced to salvage this situation. In the past, architects have used thermal mass materials to improve thermal comfort. This heavy thermal insulation could cause the time-lag effect, which might slow down the speed of heat transfer during the daytime and keep the indoor temperature within a certain range. The cool roof is low-cost technology based on solar reflectance and thermal emittance. It uses reflective materials and light colours to reflect solar radiation.
The solar reflectance and the thermal emittance are two key factors that determine the thermal performance of the roof, and they can also improve the effectiveness of the thermal insulation since around 30% solar radiation is reflected back to the sky. The shape of the roof is also under consideration, the curved roof can receive less solar energy compared with conventional shapes. Meanwhile, the drawback of this technology is obvious that the high reflectivity will cause visual discomfort. On the other hand, the high reflectivity and thermal emittance of the roof will increase the heating load of the building.
Materials and Methods of Thermal Insulation of Buildings:
There are varied forms of thermal insulation materials available in the market:
- Slab or block insulation

Block or Slab Insulation
- Blanket insulation

Blanket Insulation
- Loose-fill insulation

Loose-Fill Insulation
- Bat insulating materials

Bat Insulation
- Insulating boards

Insulation Boards
- Reflective sheet materials

Reflective Insulation
- Lightweight materials
Other General Methods of Building Thermal Insulation
Without using any thermal insulating materials as said above we can achieve the thermal insulation from the following methods.
- By providing roof shading
- By the proper height of the ceiling
- Orientation of building







