Over the past decade, human dependency on energy and resources have increased largely. We can also see the adverse effects of increased human intervention in nature. The human quest to acquire things faster than ever and to make life ‘easy’ has put a lot of stress on the resources. The abnormalities of nature that we face today is a result of overexploitation of nature and resources. The construction industry is also one of the major contributors to these abnormalities. Architecture and construction that does not resonate with nature lead to adverse effects. This is where the concept of energy-efficient architecture comes into the picture. Green architecture is a practice that relies on low consumption of resources as well as protection of nature.
How does architecture affect nature?


Construction leaves back immense impact on the environment. First of all acquiring land for construction is associated with factors that put stress on the environment. Moreover, construction techniques and materials cause further harm to the ecology. The following are the ill effects of architecture and construction on the environment:
- Acquiring of land for construction involves chopping down of trees, forests and destruction of the green cover. Also, a lot of projects involved encroachments into the farmlands, forest areas and green belts which directly contribute to the shrinking of the clean environment.
- At times, the infrastructure of national interest like damns and power station projects lead to the shifting of the indigenous communities, the ecology. This affects the indigenous flora and fauna leading to ecological imbalance.
- Encroachments on natural resources have adverse effects leading to human intervened calamities like floods and waterlogging.
- The needs of materials for construction leads to illegal and uncontrolled sand mining activities which affect the environment.
- Use of glass and concrete to a large extent dos not suit our environment and leads to increased dependency on mechanical cooling and ventilation. Thus adding extra stress on the resources.
- Mass construction reduces the green cover and increases the carbon footprint and also contributes to the emission of greenhouse gases.
- The manufacturing of non-sustainable materials, the construction of industrial projects and the emissions let out as a result of all these processes lead to pollution and harms human existence.
What is Energy-efficient Architecture?
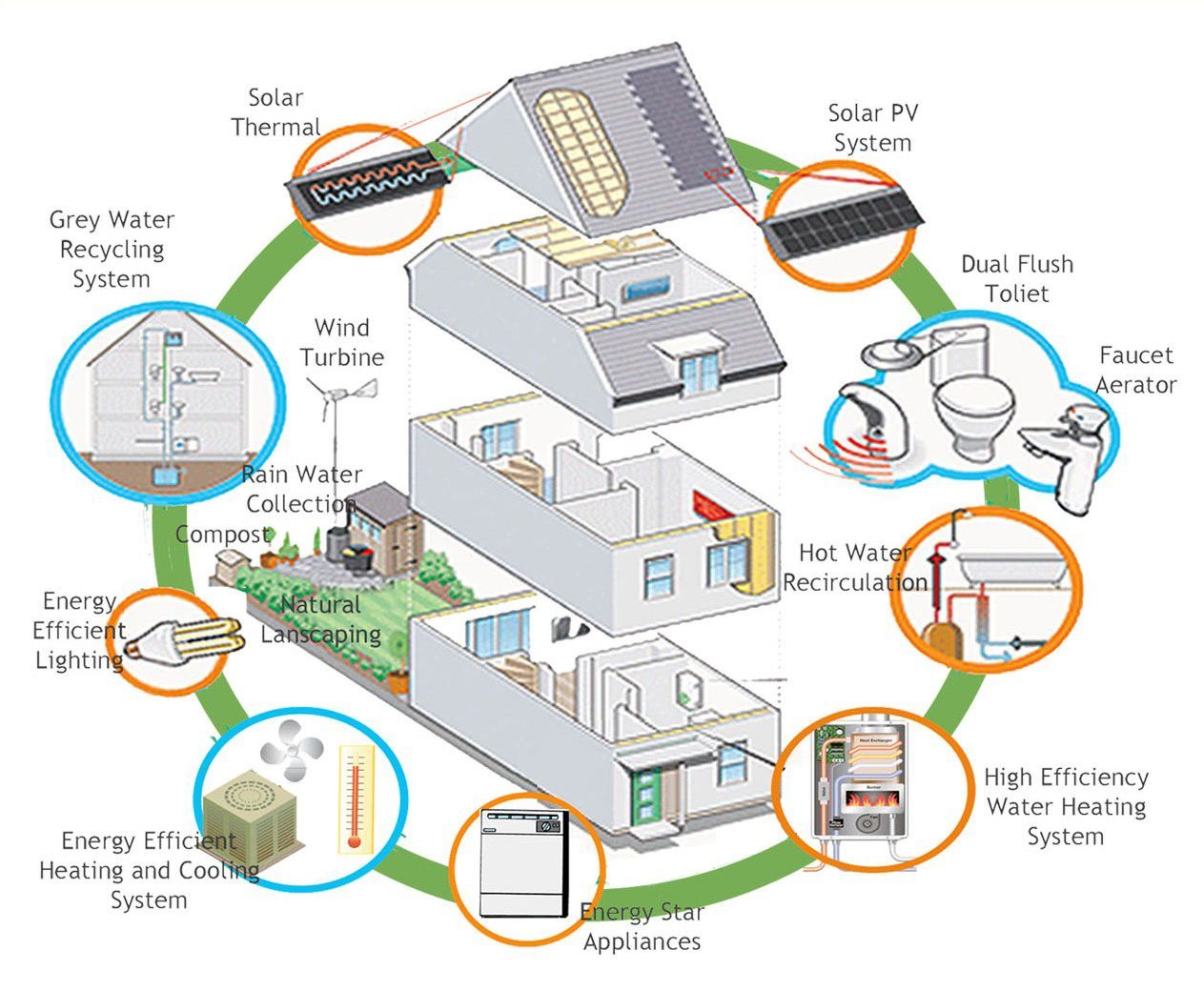

Energy-efficient architecture is an approach that helps to modulate designs that always helps to regulate the comfort zone with the minimum usage of the resources. It also involves embracing the techniques that complement the environment and usage of materials that are either reused/recycled or acquired of eco-friendly processes. Energy-efficient architecture also resonated with the environmental balance and reduces the dependency of non-renewable resources for energy. This majorly involves utilising energy that is clean and procured from natural and sustainable processes.
All of these sustainable processes are achieved in terms of various concepts of energy-efficient architecture viz. Sustainable Landscaping, Greywater reuse, Harnessing solar energy, and development of a sustainable built envelope. Energy-efficient design is based on the following constraints:
- Site constraints
- Climate
- Economy
- Social Fabric
- Material Availability
Thus, analysis if the site ad climate is important. Moreover, another important stage is an analysis of the building programme, which is based on Occupancy, Electric Lighting and Equipment influence. This is complemented with a series of techniques that form the next step. These include formulating of the bioclimatic charts, Heating pattern analysis, Passive Heating and Cooling techniques. Therefore, it could be said that a successful energy-efficient project is churned out when all these important factors fall into the right place.
Examples of Energy Efficient projects in India
One Earth by Suzlon at Pune


One Earth by Suzlon has a platinum rating for energy efficiency by LEED. The whole complex is built with low energy materials. Also, around 90 per cent of the occupied area is known to be naturally lit. It is this usage of sustainable materials and daylighting, that One Earth by Suzlon has every low carbon footprint. The exteriors of the building use renewable energy-based LED street lighting. This has led to reducing approximately 25 per cent of the total power. Whereas, the ventilation system here saves 50 per cent energy and efficiently facilitates the circulation of fresh air.
Cisco Building at Bengaluru


Cisco’s B-16 office in Bangalore has earned The LEED Platinum ID + C (Interior Design and Construction) certification. The campus is known for its recycling of 100 per cent of the generated wastewater. Moreover, the building facades have been designed with high-performance glazing as well as the energy-efficient HVAC system. The materials used for construction here is known to belong to the renewable and recycled category.



