Human settlements have always relied on food, clothing, and shelter, food is one of the most important survival entities. As the culture started evolving and settlements grew, naturally, agriculture became the prime factor around which the settlements concentrated. Fast forward to the 21st century, our population is on an alarming 7.8 billion, we have reached a point where the survival necessities demand to be revised and our cities need to be reimagined accordingly. The architectural approach towards Agriculture is an attempt to get the modern world a step closer to nature!
How does Architecture help in solving the problem?
Traditional farming needs horizontal space to cultivate and conserve the practices that go into feeding its target population. All major cities have agricultural land concentrated around them which continuously helps in covering their food requirements. By understanding the decreasing rate of available land, resources, and labor, vertical farming can be incorporated in our urban areas as an engaging activity.
Urban Agricultural Architecture or UAA is explaining to us ways in which self-sustained agricultural practices can be used in our urban areas. All Utopian ideologies in Architecture have a dedicated perspective towards agriculture and provide solutions for overcoming food shortage and its safety. These ideas need to be studied and applied in our current Architecture so as to create awareness and promote self-sustaining cities.

-
Introduce full capacity Vertical farming towers:
There are Architectural design theories that explain many ways to turn our unused niches in the cities into vertical gardens. These Gardens grow basic domestically required foods that will primarily feed the local population. There are various techniques to achieve these farms. Vertical farming either uses hydroponics or aeroponics, which reduces the amount of water used and soil required eventually reducing the load on the vertical structure. Today, it may be hard to imagine dedicated multi-storied towers for farming and food production in our cities, but it is the need of the future urban areas.
-
Converting building facades into vertical gardens:
There are many empty facades that cover our commercial and residential buildings literally serving no purpose in aesthetic or functional value in urban fabrics. Introducing vertical farming to grow plants that can feed the people accommodating the building is an innovative idea that is gaining attention today. Individual balconies can be designed to access these facades on individual floors and to maintain these vertical gardens.
-
Joint terrace farming:
Terrace gardens have been into the discussion for years now! There is an urgent need to think about converting our urban terraces to serve a purpose more important than just viewing points! Stacked trays of locally grown plants on the terraces will help in both, feeding the inhabitants and practical learning for the children.
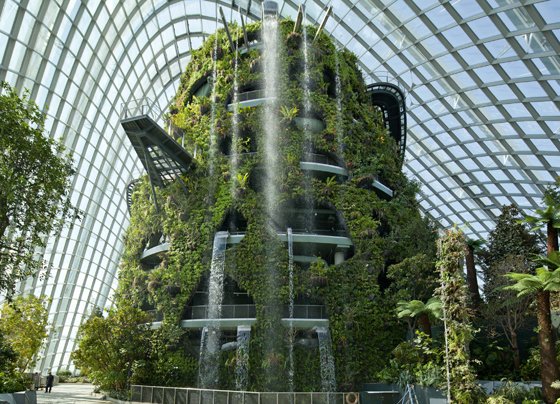

-
Adaptive Reuse:
The existing urban buildings can adapt to the technology and system of growing our own food. There are many plants that can grow in indoor temperatures and living conditions. Residential complexes, commercial centers, and restaurants can calculate their food intake within a time frame and plan their gardens accordingly in balconies and terraces. This will ensure low food wastage and awareness in people. This is a step towards sustainable and systematic development.
Advantages of introducing Agriculture in Urban Areas:
- Incorporating maximum green terrace gardening and vertical farming in cities will automatically reduce the rising urban temperature and also build a bridge between people and nature within the city boundaries. These will be the spaces where people would interact as well as work together towards a collective goal.
- Increased number of plants means increased air quality and green spaces. These will allow people of the cities to step outside and enjoy their time in nature!
- The unused spaces in the city will serve a purpose and can be accommodated for growing the local food. This will ensure the safe use of the neglected areas and increased environmental conditions of the surrounding areas.
- Building greenhouses on the deserted open grounds will connect these spaces back with the city. They could be a part of local school projects or be an income source for the local community.
Agricultural modules in Architectural fabrics are being experimented by all designers in ways like stepped gardens, modular vertical gardens, and super-farms. It is modern, easy and utilizes less energy to grow maximum food supplies in minimum spaces!