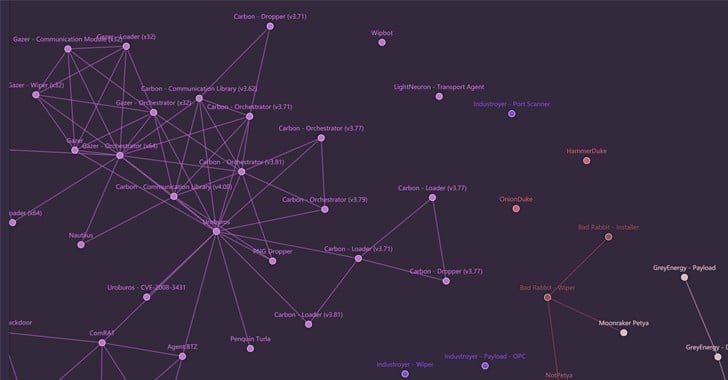
Russian APT Map (Check it out here), a connection which is used to learn about the links between various APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) malware samples, malware families and hackers – all with one click on the map nodes. To illustrate a bigger picture and make it accessible and more comfortable for everyone to understand the Russian hackers and their operations, researchers from Intezer and Check Point Research jointly released a web-based interactive map which gives a full overview of the ecosystem.
It is a web-based interactive map which shows different families and actors that are a part of the Russian APT ecosystem, as well as the connections between them. The Map can be said to be one-stop for anyone interested to learn and understand the links and attributions of the samples, modules, families that together constitute the ecosystem.
The Map is so rich with information that the user can get a full overview fo the ecosystem with specific connections about the malware families of which node belongs to whom as well as the links to analyze reports. The key findings included thousands of samples classified and analyzed to map connections between different cyber-espionage organizations of Russia. Every organization under the Russian APT umbrella has its dedicated malware toolkits and frameworks. Gathering samples, Classifying the samples, Similarities between the samples, and Analyzing the identified connections were the significant attributes that are encountered during the analysis and investigation.
The Russian APT Map also revealed in spite of most hacking teams are reusing their code in their different tools and contexts, no different groups were found using each other’s code, in this way the risk of damage of hacking business exposed the other active actors, preventing the collapses of a well-structured ecosystem.
The Russian APT Map resulted in encyclopedic research where the researchers gathered, classified and analyzed more than 2,000 malware samples associated to the Russian hacking organizations and mapped approximately 22,000 interconnections between them based on3.85 million pieces of code they shared. The examples fall into 60 families and 200 different modules as per the analysis. To make the data more efficient and advance in the near future, the researchers have also open-sourced the Map and the data behind it.
The research added to growing evidence of Russia’s ongoing efforts to step up the operational security, overcoming a “compromised operation to expose other active operations.” The analysis revealed that malware and code shared among the actors is found and the credential acquisition software distributed by the forums. The functional difference between the two actors was found to be self-deleting developed by each of the actors, found to be rare for codes to be shared between different actors or organizations. According to the researchers, common codes were seen between different projects of the same actor, and sharing the code is organized within the same actor, implying that they are aware of the mutual work situation.

There are two theories which were used for analyzing, even though the malware has the same purpose, each actor develops it individually to make sure the repetition and there is no mutual cooperation due to political disputes between organizations which supports the actors.
Having access to more than 3.5 Million codes that were shared between the Russian APT samples gathered, allowed Intezer to understand the unique genes that more likely were shared between samples, families, and actors. It benefitted the organization to write a tool that can be used by organizations, CERT teams, researchers, and individuals to scan a specific file, a folder, or a whole file system, and search for infections by Russian APTs. The tool is named as Russian APT Detector, a set of Yara rules produced by Intezer’s platform. The rules contain byte-sequences of popular mutual codes between one or more samples which were further wrapped in a binary to ease the use of the tool. The full rules can be found in this repository and can be used freely on Yara scanner.
As a result, the obscurity behind the complex coding and operations had made us establish a known fact that even after a lot of information about single actors, we are short of seeing an entire ecosystem with actor interaction which can be viewed on a much larger scale. According to Intezer, this research is the first and most comprehensive of its kind. for the first time, thousands of samples were gathered, classified and analyzed in order to map connections between different cyber- organizations of Russia.
Source: Intezer
For more Information: https://www.intezer.com/blog-russian-apt-ecosystem/